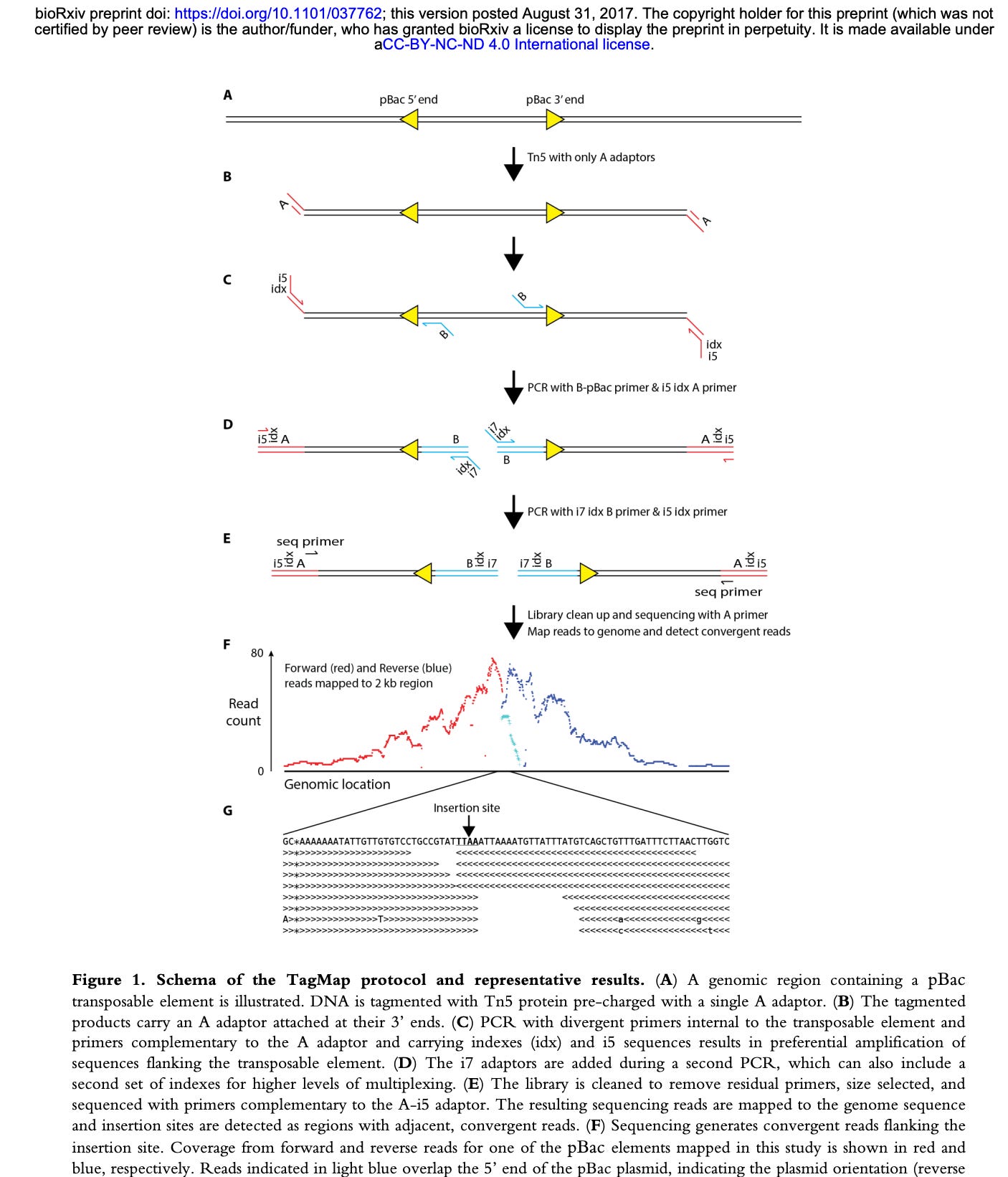
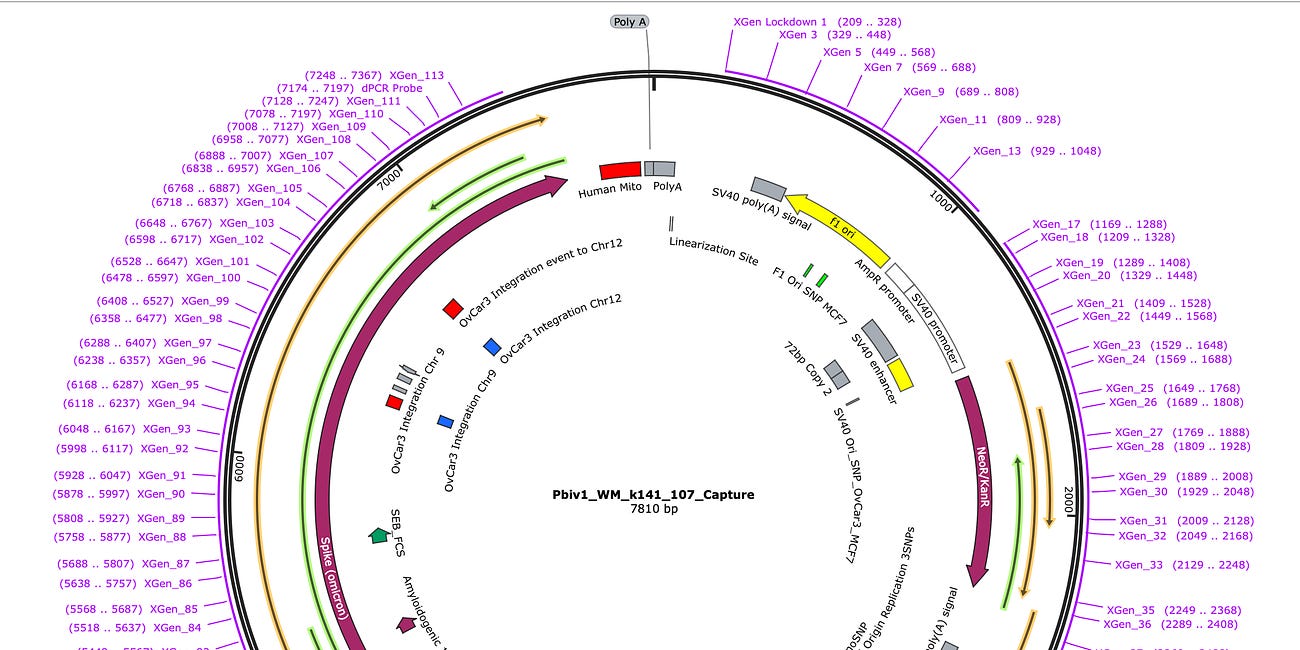
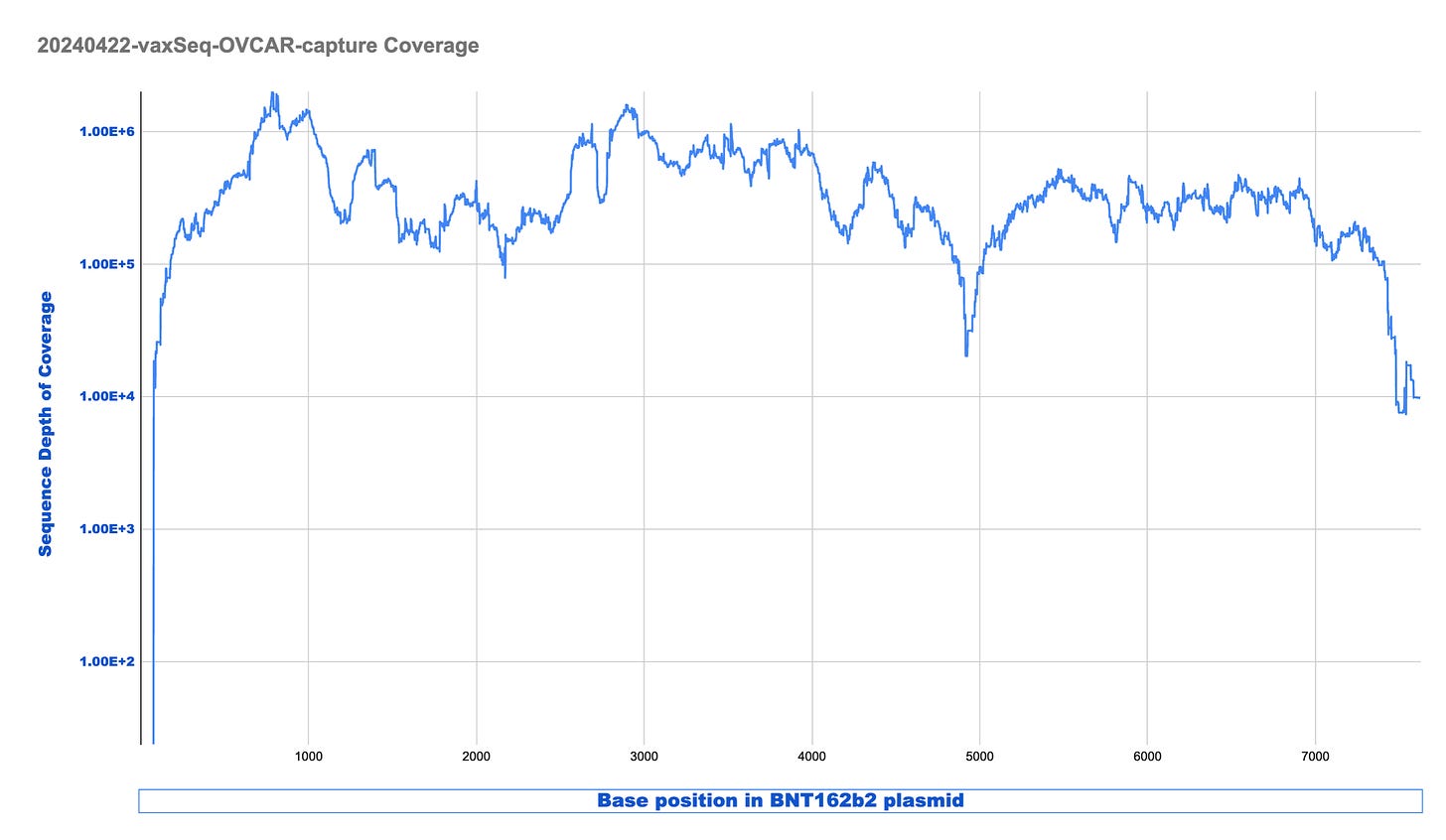
Parts of this did not copy exactly right. I apologize. On my phone but thought this needed to be be posted.
Doctors Predict Epidemic of Prion Brain Diseases
Analysis by Dr. Joseph Mercola April 29, 2024
STORY AT -A-GLANCE
According to mounting data, one of the more serious side effects of the COVID mRNA
jabs appears to be dementia, and worse yet, this previously untransmissible disease
may now be “contagious, ” transmissible by way of prions.
In my 2021 interview with Stephanie Seneff, Ph.D., she explained why she suspected the
COVID shots may eventually result in an avalanche of neurological prion-based diseases
Doctors Predict Epidemic of Prion Brain Diseases
Analysis by Dr. Joseph Mercola April 29, 2024
Mounting research suggests a serious side effect of the COVID mRNA jabs could be
dementia, and the prions that cause it may be contagious
Frameshifting, as we now know occurs in the COVID shots, can induce prion production
and lead to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Creutzfeldt-Jakob
disease (CJD)
Sid Belzberg's prions.rip website, which collected data on neurological side effects post-
jab, found a notably high incidence of diagnosed CJD cases, suggesting an alarming
trend
A series of articles highlight biases in clinical trials and observational studies, suggesting
COVID-19 vaccines' safety and effectiveness have been massively overstated
The Global COVID Vaccine Safety Project study — funded by the U.S. Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention — reveals significant side effects, including myocarditis,
pericarditis, and blood clots, underscoring the need for reevaluation of COVID vaccine
risks and benefits
such as Alzheimer’s. She also published a paper detailing those mechanisms in the May
10, 2021, issue of the International Journal of Vaccine Theory. As she explained in that
paper:
“A paper published by J. Bart Classen (2021) proposed that the spike protein in
the mRNA vaccines could cause prion-like diseases, in part through its ability to
bind to many known proteins and induce their misfolding into potential prions.
Idrees and Kumar (2021) have proposed that the spike protein’s S1 component
is prone to act as a functional amyloid and form toxic aggregates ... and can
ultimately lead to neurodegeneration. ”
In summary, the take-home from Seneff’s paper is that the COVID shots, offered to
hundreds of millions of people, are instruction sets for your body to make a toxic protein
that will eventually wind up concentrated in your spleen, from where prion-like protein
instructions will be sent out, leading to neurodegenerative diseases.
What Are Prions?
The term "prion" derives from "proteinaceous infectious particle. " Prions are known to
cause a variety of neurodegenerative diseases in animals and humans, such as
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) in humans, bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE or
"mad cow disease") in cattle, and chronic wasting disease in deer and elk.
These diseases are collectively referred to as transmissible spongiform
encephalopathies (TSEs). They’re characterized by long incubation periods, brain
damage, the formation of holes in the brain giving it a sponge-like appearance, and
failure to induce an inflammatory response.
“Infectious prions propagate by transmitting their
misfolded protein state to normal variants of the same
protein.”
1
In short, prions are infectious agents composed entirely of a protein material that can
fold in multiple, structurally distinct ways, at least one of which is transmissible to other
prion proteins, leading to a disease that is similar to viral infections but without nucleic
acids.
Unlike bacteria, viruses, and fungi, which contain nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) that
instruct their replication, prions propagate by transmitting their misfolded protein state
to normal variants of the same protein.
According to the prion disease model, the infectious properties of prions are due to the
ability of the abnormal protein to convert the normal version of the protein into the
misfolded form, thereby setting off a chain reaction that progressively damages the
nervous system.
Prions are remarkably resistant to conventional methods of sterilization and can survive
extreme conditions that would normally destroy nucleic acids or other pathogens, which
is part of why prion diseases are so difficult to treat.
More Evidence mRNA Shots Can Trigger Dementia
Today, there’s even more evidence to support Seneff’s theory. In August 2022, tech
entrepreneur Sid Belzberg wrote about prions.rip, a website he’d set up to collect data
on the neurological side effects of the jabs. (This site is no longer live.)
Within a few months, the site had received about 15,000 hits and gathered 60 reports
from people who got the jab and suffered neurological deficits shortly thereafter,
including six cases of diagnosed CJD.
“Normally this disease affects 1 in a 1,000,000 people, ” Belzberg wrote. “To get
6 cases you would need 6,000,000 hits to the site assuming everyone reports.
The chances of getting 1 case in 15,000 hits is 1 in 66. To see 6 cases in 1
group of 15,000 is 1/66^6 or 1 in 82,000,000,000, or 20 times more likely to win
a Powerball lottery! ...
2
3
To reiterate, CJD is an exceptionally rare disease that is now a known and
established severe adverse reaction (SAE) from the DEATHVAX™. Injecting this
slow kill bioweapon can cause ailments that are about as likely to develop in the
real word as getting struck by lightning twice. The proof is now irrefutable. ”
Frameshifting Can Result in Prion Production
In mid-December 2023, researchers reported that the replacing of uracil with
synthetic methylpseudouridine in the COVID shots — a process known as codon
optimization — can cause frameshifting, a glitch in the decoding, thereby triggering the
production of off-target aberrant proteins.
The antibodies that develop as a result may, in turn, trigger off-target immune reactions.
According to the authors, off-target cellular immune responses occur in 25% to 30% of
people who have received the COVID shot. But that’s not all.
According to British neuroscientist Dr. Kevin McCairn, this frameshifting phenomenon
has also been linked to harmful prion production — and that frame shifted prions,
specifically, are infectious and can be transmitted from one person to another. As
reported in the Journal of Theoretical Biology in 2013:
“A quantitatively consistent explanation for the titres of infectivity found in a
variety of prion-containing preparations is provided on the basis that the
etiological agents of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy comprise a very
small population fraction of prion protein (PrP) variants, which contain
frameshifted elements in their N-terminal octapeptide-repeat regions ...
Frameshifting accounts quantitatively for the etiology of prion disease. One per
million frameshifted prions may be enough to cause disease. The HIV TAR-like
element in the PRNP mRNA is likely an effector of frameshifting. ”
McCairn explained this mechanism in a February 19, 2023, interview with Health
Alliance Australia (video above). In it, he noted:
4,5,6
7
“Mis-folded proteins caused by prions can impact every level organ and tissue
system in the body ... [They] bioaccumulate and are resistant to degradation,
thereby building up ... ”
Prions may in fact be the primary molecule that is being “shed” by COVID jab recipients,
and if those prions are due to frameshifting, that could be very bad news indeed,
considering their implication in dementia.
Another doctor who believes we’ll be facing an “epidemic of prion disease” is Dr. David
Cartland. In late February 2024, he posted 13 scientific papers linking the COVID jabs,
prion diseases and CJD, noting that was just a “small selection” of what’s available in the
medical literature.
Prions Implicated in Long COVID as Well
According to genomics expert Kevin McKernan, Ph.D., prions are also involved in long
COVID (or as McKernan calls it, “long vax”). In one 2024 study, 96.7% of long COVID
sufferers had received the jab. In an interview with the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care
Alliance (FLCCC), McKernan stated:
“If you frameshift over the stop codons, you’re going to be making proteins that
are spike-mito proteins. When I talk to a lot of the long vax patients I hear of all
these things that remind me of my time in the mitochondrial disease
sequencing space ... ”
McKernan claims he tried to publish a paper on this in 2021 with Dr. Peter McCullough,
but the editor of the journal “stepped in and torpedoed the paper.
”
World’s Largest Side Effect Analysis Has Been Published
In related news, the largest study to date on the side effects of the COVID jabs was
published in the journal Vaccine in February 12, 2024, and it confirms what I and many
8
9 10
11
12
13
other alternative news sources have been saying all along, namely that the mRNA jabs
are the most dangerous medical products to ever hit the market.
The study — performed by the Global COVID Vaccine Safety (GCoVS) Project and funded
by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Public Health Ontario and the
Canadian Health Research Institute — evaluated the risk of "adverse events of special
interest" (AESI) following COVID-19 “vaccination. ”
Data from 10 sites in eight countries (Argentina, Australia, Canada, Denmark, Finland,
France, New Zealand and Scotland) were included, encompassing more than 99 million
jabbed individuals.
Of the thousands of side effects Pfizer listed in its confidential report of post-
authorization adverse events submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the
GCoVS focused on 13 AESIs that fall into three primary categories: Neurological,
hematologic (blood-related) and cardiovascular conditions.
They calculated the AESI risk for each of the 13 AESIs based on the number of observed
versus expected (OE) incidents occurring up to 42 days after injection. The “expected”
number of side effects were based on vaccine adverse event data from 2015 to 2019.
These rates were then compared to the adverse event rates observed in those who got
one or more of the COVID jabs, either Pfizer's BNT162b2, Moderna's mRNA-1273, or
AstraZeneca's ChAdOx1.
Largest Study to Date Confirms COVID Jab Dangers
The analysis revealed several concerning side effects, including increased risks of
myocarditis, pericarditis, blood clots in the brain, and various neurological conditions.
Here’s a quick summary of the findings:
• Myocarditis and pericarditis:
◦ Pfizer vaccine — OE ratios for myocarditis were 2.78 and 2.86 after the first
and second shots, with the risk remaining doubled after the third and fourth
14
15
shots.
◦ Moderna vaccine — OE ratios for myocarditis were 3.48 and 6.10 after the first
and second shots. Doses 1 and 4 also showed OE ratios of 1.74 and 2.64 for
pericarditis.
◦ AstraZeneca vaccine — OE ratio for pericarditis was 6.91 after the third shot.
• Blood clots in the brain (cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, CVST):
◦ An OE of 3.23 for CVST was observed after the first AstraZeneca shot.
◦ A significant increase in CVST risk was also noted after the second Pfizer dose.
• Neurological conditions:
◦ Guillain-Barré syndrome — An OE ratio of 2.49 was observed following the
AstraZeneca jab.
◦ Transverse myelitis — Risk nearly doubled with the AstraZeneca shot.
◦ Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis — OE ratios of 3.78 (Moderna) and 2.23
(AstraZeneca) were noted.
These findings really underscore the potential for serious side effects from the COVID
shots, including conditions that may lead to other consequences in the longer term,
such as stroke, heart attack, paralysis and death.
Effectiveness and Safety Was Wildly Exaggerated in Trials
Considering those findings, it’s no surprise to find that effectiveness and safety were
exaggerated in clinical trials and observational studies. In a guest post on Dr. Robert
Malone’s Substack, Raphael Lataster, Ph.D., writes:
“An unofficial series of four crucially important medical journal articles, two by
me, appearing in major academic publisher Wiley’s Journal of Evaluation in
Clinical Practice reveals that claims made about COVID-19 vaccines’
16
effectiveness and safety were exaggerated in the clinical trials and
observational studies, which significantly impacts risk-benefit analyses.
Also discussed are the concerning topics of myocarditis, with evidence
indicating that this one adverse effect alone means that the risks outweigh the
benefits in the young and healthy; and perceived negative effectiveness, which
indicates that the vaccines increase the chance of COVID-19
infection/hospitalization/death, to say nothing about other adverse effects. ”
Summary of Papers
The four papers in question include:
1. “Sources of Bias in Observational Studies of COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness”
published in the Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice in March 2023, co-
authored by BMJ editor Peter Doshi, Ph.D., statistician Kaiser Fung and
biostatistician Mark Jones, which concluded that “case-counting window bias” had
a significant effect on effectiveness estimates.
As explained by Lataster, this “concerns the 7 days, 14 days, or even 21 days after
the jab where we are meant to overlook jab-related issues, such as COVID
infections, for some odd reason as ‘the vaccine has not had sufficient time to
stimulate the immune system. ’
This may strike you as quite bizarre since all of the ‘fully vaccinated’ must go
through the process of being ‘partially vaccinated, ’ sometimes even more than once.
To make matters worse, the unvaccinated do not get such a ‘grace period, ’ meaning
that there is also a clear bias at play.
In an example using data from Pfizer’s clinical trial, the authors show that thanks to
this bias, a vaccine with effectiveness of 0%, which is confirmed in the hypothetical
clinical trial, could be seen in observational studies as having effectiveness of 48%. ”
17
2. “Reply to Fung et. al. on COVID-19 Vaccine Case-Counting Window Biases
Overstating Vaccine Effectiveness, ” authored by Lataster, which discussed how the
counting window bias not only affected effectiveness estimates in observational
studies but also safety estimates, suggesting a need for reassessment of vaccine
safety. The article also addresses “the mysterious rise in non-COVID excess
deaths post-pandemic. ”
3. “How the Case Counting Window Affected Vaccine Efficacy Calculations in
Randomized Trials of COVID-19 Vaccines, ” again co-authored by Doshi and Fung,
which detailed how case-counting window issues also overestimated effectiveness
in Pfizer and Moderna clinical trials.
4. A second article by Lataster, in which he highlighted and summarized the evidence
showing that clinical trials were affected by adverse effect counting window issues
that led to exaggerated safety estimates.
“Together, these four articles make clear that claims made about COVID-19 vaccines;
effectiveness and safety were exaggerated in the clinical trials and observational
studies, whilst also finding time to discuss myocarditis and perceived negative
effectiveness, meaning that new analyses are very much needed, ” Lataster writes.
Resources for Those Injured by the COVID Jab
Based on data from across the world, it’s beyond clear that the COVID shots are the
most dangerous drugs ever deployed. If you already got one or more COVID jabs and are
now reconsidering, you’d be wise to avoid all vaccines from here on, as you need to end
the assault on your body. Even if you haven’t experienced any obvious side effects, your
health may still be impacted long-term, so don’t take any more shots.
If you’re suffering from side effects, your first order of business is to eliminate the spike
protein — and/or any aberrant off-target protein — that your body is producing. Two
remedies shown to bind to and facilitate the removal of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein are
hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin. I don’t know if these drugs will work on off-target
proteins and nanolipid accumulation as well, but it probably wouldn’t hurt to try.
18
19
20
21
22
The Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC) has developed a post-vaccine
treatment protocol called I-RECOVER. Since the protocol is continuously updated as
more data become available, your best bet is to download the latest version straight
from the FLCCC website at covid19criticalcare.com.
For additional suggestions, check out the World Council for Health’s spike protein detox
guide, which focuses on natural substances like herbs, supplements and teas. Sauna
therapy can also help eliminate toxic and misfolded proteins by stimulating autophagy.
Sources and References
International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice and Research May 10, 2021; 2(1): 402-444
2ndsmartestguyintheworld.com August 18, 2022
Nature December 6, 2023
Trial Site News December 7, 2023
The Telegraph December 6, 2023
Journal off Theoretical Biology May 2013; 325: 52-61
Twitter/X Dr. David Cartland February 24, 2024
LifeSite News March 4, 2024
Journal of Clinical Medicine 2024; 13(5): 1208
Vaccine February 12, 2024 [epub ahead of print]
5.3.6 Cumulative Analysis of Post-Authorization Adverse Event Reports Received Through 28-Feb-2021,
Pages 30-38
RW Malone MD Substack March 6, 2024
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice March 26, 2023; 30(1): 30-36
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice July 4, 2023; 30(1): 82-85
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice July 15, 2023; 30(1): 105-106
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice January 18, 2024
Covid19criticalcare.com
World Council for Health Spike Protein Detox Guide November 30, 2021