www.theepochtimes.com
(fair use applies)
EXCLUSIVE: Former Harvard Prof. Martin Kulldorff: ‘Science and Public Health Are Broken’
By Charlotte Cuthbertson
February 16, 2022 | Updated: February 18, 2022
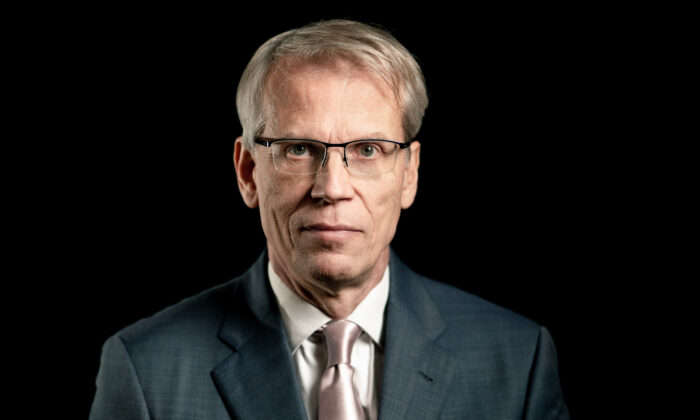
Dr. Martin Kulldorff is one of the most qualified public health pandemic experts in the United States. To the narrative-shapers, he’s a pariah.
As a prominent epidemiologist and statistician, Kulldorff has worked on detecting and monitoring infectious disease outbreaks for two decades. His methods are widely used around the world and by almost every state health department in the United States, as well as by hundreds of people at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Kulldorff has also worked on vaccine safety for decades, developing globally used methods for monitoring adverse reactions in new vaccines.
His résumé on the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website is 45 pages long and includes a list of 201 peer-reviewed published journal papers. His work has been cited more than 27,000 times.
Since 2003, Kulldorff worked at Harvard Medical School, first as an associate professor of population medicine and later as a professor of medicine.
In November, Harvard and Kulldorff abruptly parted ways.
Kulldorff prefers to keep the reasons private, but it’s hard to ignore that he placed himself in the crosshairs of the pandemic narrative early on in the “15 days to slow the spread” lockdown and has since paid the price.
It’s quite something for a public health scientist at the top of his game to admit that “both science and public health are broken.”
“For some reason, a public official narrative was established, and you weren’t allowed to question it—which, of course, is very detrimental, both to the pandemic and how to deal with the pandemic, because you have to have a vibrant discussion to figure out how best to deal with these things,” he told The Epoch Times.
The Swedish native said he tried to point out in March 2020 that there was a very steep age gradient on mortality for COVID-19, the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Kulldorff said he attempted to publish a paper both in U.S. medical journals and mainstream newspapers stating that while anyone could contract the virus, the focus should be on protecting the elderly and those at high risk. His paper was knocked back from all directions.
“I was able to publish in Sweden, in the major daily newspapers there during the spring of 2020, so that was not a problem,” he said. “But the United States was not allowed to have a debate, which is very troubling.”
The Great Barrington Declaration
His early efforts culminated in the
Great Barrington Declaration, published with Dr. Sunetra Gupta and Dr. Jay Bhattacharya in October 2020. The declaration called for a more nuanced approach to the one-size-fits-all restrictions that had been imposed on much of Western society.
“The most compassionate approach that balances the risks and benefits of reaching herd immunity, is to allow those who are at minimal risk of death to live their lives normally to build up immunity to the virus through natural infection, while better protecting those who are at highest risk,” the declaration states.
The two other authors are also amply qualified in the field. Gupta is a professor at Oxford University, an epidemiologist with expertise in immunology, vaccine development, and mathematical modeling of infectious diseases. Bhattacharya is a professor at Stanford University Medical School, a physician, epidemiologist, health economist, and public health policy expert focusing on infectious diseases and vulnerable populations.
Kulldorff said the Great Barrington Declaration proposed nothing new.
“It’s just the basic fundamental principles of public health that existed in the pandemic preparedness plan that was prepared many years before,” he said. “It’s sort of astonishing that it wasn’t followed from the very beginning of the pandemic.”
Conventional public health science had deemed it unnecessary and potentially harmful to close schools and small businesses, to impose masking on the general public, and to quarantine healthy people.
Kulldorff said the document wasn’t for the politicians, or scientists, or even the doctors—although thousands of each signed it.
“The most important audience was the public,” he said, “because it’s the public that ultimately will end these misguided public health policies. It’s the public, regular people, who are suffering the consequences.”
He said the authors wanted to advise the average person that their intuition was correct, that the restrictions weren’t based on public health science—”so when you oppose them, you’re standing on firm scientific ground.”
“The key thing was to break the pretense that there was scientific consensus for these lockdowns—which there wasn’t.”
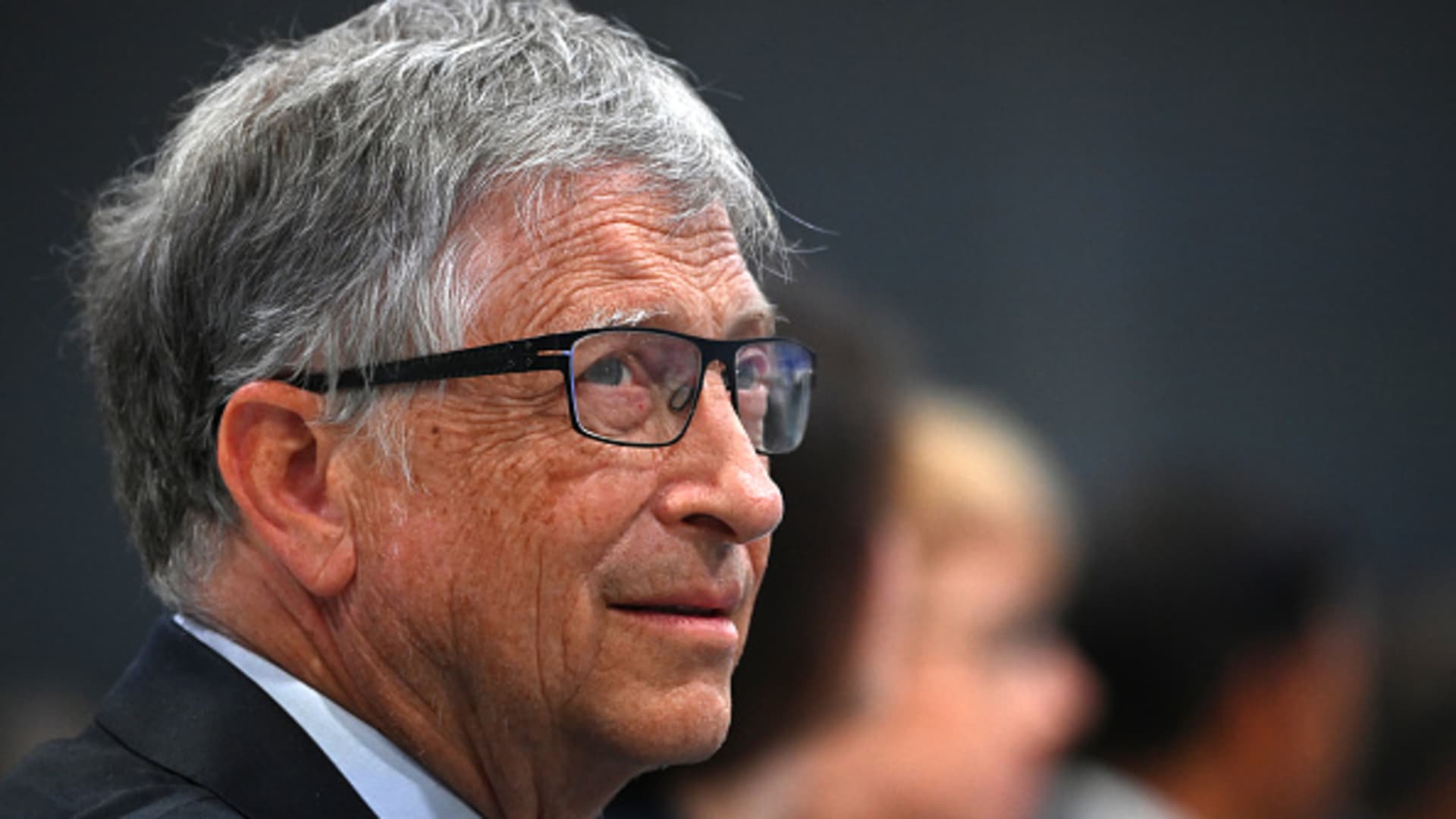
The appearance of a scientific consensus was formed through high-profile public health officials such as Dr. Anthony Fauci, Dr. Francis Collins, and Dr. Deborah Birx, as well as corporate media along with the stifling of opposing viewpoints.
“There’s really no public health arguments against the declaration. So if you want to criticize it, you have to … make up lies about it and then attack that, as well as slander the people behind it. And they did both of those things,” Kulldorff said.
It wasn’t until a December 2021 email dump that Kulldorff and the American public
got to peek behind the curtain of how the traditional pandemic playbook had been tossed and how swiftly dissenting voices were maligned.
Following a Freedom of Information Act request, emails that involved Fauci, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), were released. An email to Fauci from Collins, then-director of the National Institutes of Health, was sent days after the Great Barrington Declaration was published.
“This proposal from the three fringe epidemiologists … seems to be getting a lot of attention,” Collins told Fauci in the Oct. 8, 2020, email. “There needs to be a quick and devastating published takedown of its premises. I don’t see anything like that online yet—is it underway?”
Collins’s four-line
email mentioned that the declaration included “even a co-signature from Nobel Prize winner Mike Leavitt at Stanford.”
Fauci appears to have been in full agreement with Collins’s proposal to take down the authors and their declaration, sending a one-line reply.
“I am pasting in below a piece from the Wired [magazine] that debunks this theory,” he wrote. Collins replied. “Excellent.”
Within a day of the Collins–Fauci exchange, Google began to censor search results for “Great Barrington Declaration.”
In a subsequent interview, Collins said the declaration “is not mainstream science. It’s dangerous.”
Fauci called the declaration “ridiculous” and “total nonsense” in an interview with ABC.
A cavalcade of articles from corporate media outlets ensued, with a common theme to disparage the declaration and its authors.
The New York Times called focused protection a “viral theory.”
BuzzFeed called it a “highly controversial recommendation.”
Forbes called the declaration’s detractors “real infectious disease and public health experts.”
“Anti-lockdown advocate appears on radio show that has featured Holocaust deniers,” a Guardian headline blared, referring to Kulldorff’s interview on the “Richie Allen Show.”
Gregg Gonsalves, an associate professor of epidemiology at Yale, called the focused protection strategy “a massacre” and a “straw man argument” produced by “fancy scientists,” in a Twitter
thread a week after the declaration was published.
Kulldorff, when asked if he’d ever considered himself a “fringe epidemiologist,” said, “No I have not, but I guess, when the public health leaders get it wrong, then it’s an honor to be a fringe epidemiologist.”
Social media giants such as Twitter and Facebook jumped on the censorship bandwagon and started labeling certain posts as misleading, while permanently banning journalists such as Alex Berenson.
Berenson’s final tweet before being purged was about the COVID-19 vaccines.
“It doesn’t stop infection. Or transmission,” he posted on Aug. 28, 2021. “Think of it—at best—as a therapeutic with a limited window of efficacy and terrible side effect profile that must be dosed in advance of illness. And we want to mandate it? Insanity.”
Berenson, a former New York Times journalist, has since
sued Twitter.
“You always have to be allowed to question science,” Kulldorff said. “We should never silence that debate, pretend that there’s some person who is ‘The Science,’ who has all the truths.
“I think that happened during this pandemic and that’s an embarrassment for the scientific community.”
In an interview at the end of November 2021, Fauci
lashed out at Republican senators who had criticized him.
“They’re really criticizing science, because I represent science,” Fauci told CBS.
Personal Life
Kulldorff was 8 years old when he first came to reside in the United States. His father, also a scientist, moved the family from Sweden for a one-year university sabbatical in 1970.
It was October, and two weeks after arriving in Texas, Kulldorff’s mother told him to don a costume and head out with the local children.
“We walked around the neighborhood, and everywhere we knocked on the door, they gave us candy. So that was pretty nice for an 8-year-old. And I’ve liked this country ever since,” he said.
Kulldorff returned to the United States for a couple of years in the 1980s for his doctoral work, and in the early ’90s, he made the move permanent.
The original dream for Kulldorff was to teach high school math and history. He laughs about it still being a backup plan if his current career falls apart.
He still sees fatherhood as his most important job. As a single father with a 19-year-old son and twin 6-year-olds, he spends a lot of time with his children.
“I think the most wonderful and the most important thing in life is to be a parent and see your children grow up,” he said. “So I have always spent plenty of time with them since they were born. I’ve always prioritized that over my career.”
He said the twins were fortunate during the pandemic restrictions in Connecticut to have each other as built-in playmates.
His oldest son was 17 when the pandemic started.
“I wasn’t concerned about him getting COVID because I knew that the risk for him is minuscule. But I was very concerned about his mental health. So I was urging him to go out there and play basketball with his friends, hang out with them, do those social things. I wanted him to have as normal a life as possible.”
Why Take a Stand?
Kulldorff has worked in both the Swedish and U.S. health science fields, and followed closely his native country’s very different, less invasive response to the pandemic.
His family members in the Nordic country understood when he took a divergent tack to the U.S. mainstream narrative of harsh lockdowns, closing schools, and mandatory masking.
“Sweden had a more sane approach to it, so they didn’t find it strange what I was saying,” he said.
He didn’t set out to be a rebel, and there wasn’t much hand wringing behind Kulldorff’s decision to go against the grain when he saw the tried-and-true pandemic response being cast aside.
“I don’t think I have a choice. Since I worked on infectious disease outbreaks for two decades and they instituted policies that go against the basic principles to public health, I can’t just be silent. I have to speak up. There’s no other alternative,” he said.
“Otherwise, what’s the point of being a public health scientist?”
He’s quick to show support for other scientists who agree with him but feel as if they can’t speak out due to potential loss of research funding or even their job. People such as Fauci, who oversees an annual taxpayer-funded
budget of over $6 billion at NIAID, hold the purse strings as well as control of what’s published in journals.
“If you dare speak out against [Fauci’s] views on the pandemic, you can lose funding. And if you agree with him and support him, you can gain funding,” Kulldorff said.
Four prominent scientists who were instrumental in shaping the COVID-19 “natural origin” narrative received substantial
increases in grant money from Fauci’s NIAID in the subsequent two years, The Epoch Times found.
“So I fully understand that scientists are very afraid of criticizing the policies championed by the guy who sits on the biggest chunk of infectious disease research money in the world,” Kulldorff said.
“We shouldn’t have those conflicts. Research should be very broad, and we should fund broadly different ideas, and some pan out and some don’t, but that’s how you do good science.”
Collateral Damage
One of the major precepts behind the Great Barrington Declaration is that public health is wide-ranging and needs a long-term view, yet many influential scientists had a singular focus on COVID-19 outcomes.
“One of the principles of public health is, it’s not about one disease, like COVID, it’s about all of public health,” Kulldorff said.
That singular focus resulted in government officials filling skateboard parks in California with sand and locking up children’s playgrounds with chains and yellow police tape. Millions of children were sent home from school and for almost two years were forced to learn virtually from home.
Meanwhile, teen suicide rates have increased, drug and alcohol abuse has increased, domestic violence has risen, while childhood vaccinations decreased and cancer screenings plummeted.
Health experts
warned in May 2020 that as pandemic-driven hardship puts added strain on the mental health of Americans, as many as 154,000 extra lives may be lost due to drug or alcohol abuse and suicide, or “deaths of despair.”
People were dying from cardiovascular diseases that, in normal circumstances, they would have survived, Kulldorff said,”because maybe they were afraid to go to the hospital, or they went too late.”
“So these are all tragic consequences, collateral damage, of these COVID measures, restrictions that were imposed,” he said. “And you can’t just do that for a whole year or two and expect that it doesn’t have other enormously bad outcomes on public health.”
Kulldorff anticipates that many of the ancillary health impacts have yet to surface.
In January, a Johns Hopkins meta-analysis of lockdown data
concluded that lockdowns didn’t save lives.
What’s Next?
Kulldorff is dedicating his next chapter to helping restore trust in science and public health—both of which he calls “broken.”
“So it’s the heads of the funding agencies, the heads of the big journals, and the university presidents and deans who all went into the same bubble thinking that they knew what was right, and which turned out to be wrong,” Kulldorff said.
“But all scientists now are going to have to suffer from that, because, for good reasons, the public won’t trust scientists anymore.”
He’s working with the Brownstone Institute as the scientific director to navigate how to shore up public health again. He’s also part of Hillsdale College’s new Academy for Science and Freedom, which he says will promote and defend the importance of open, free scientific discourse.
“It’s very clear that if we want to have vibrant science, and a vibrant scientific community, we have to reform the way science operates and the way public health operates,” he said.
But, Kulldorff said, it’s up to the public—the truckers, farmers, nurses, pilots, and parents—as well as rank-and-file scientists to effect real change.
It’s also time to compassionately help each other heal from the psychological and mental wounds, he said, especially those still living in constant fear of COVID and those who have been self-isolating for two years now.
“I think we shouldn’t blame those who were afraid, because they were major victims of this pandemic strategy,” he said.
“We shouldn’t blame people for believing Anthony Fauci and the CDC—that was the natural thing to do. We just have to help them realize that these measures were misguided so that never happens again.”






/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/BCCMJNF3HFLOBN66DWLIPL24KM.jpg)